Google Scholar Page
Publications in this page: Bold font indicates serving as first or corresponding author.
0 Intelligent Robot
|
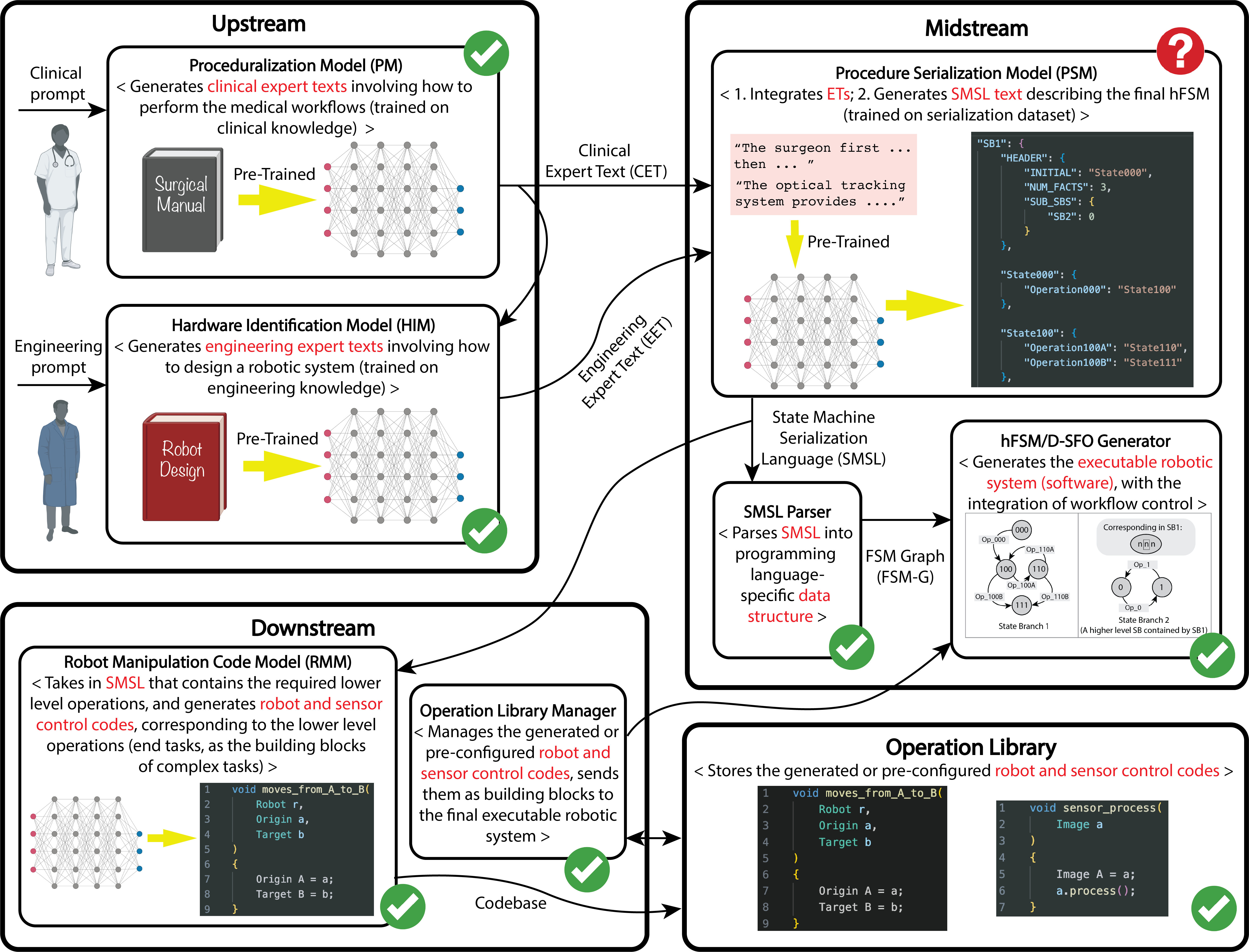
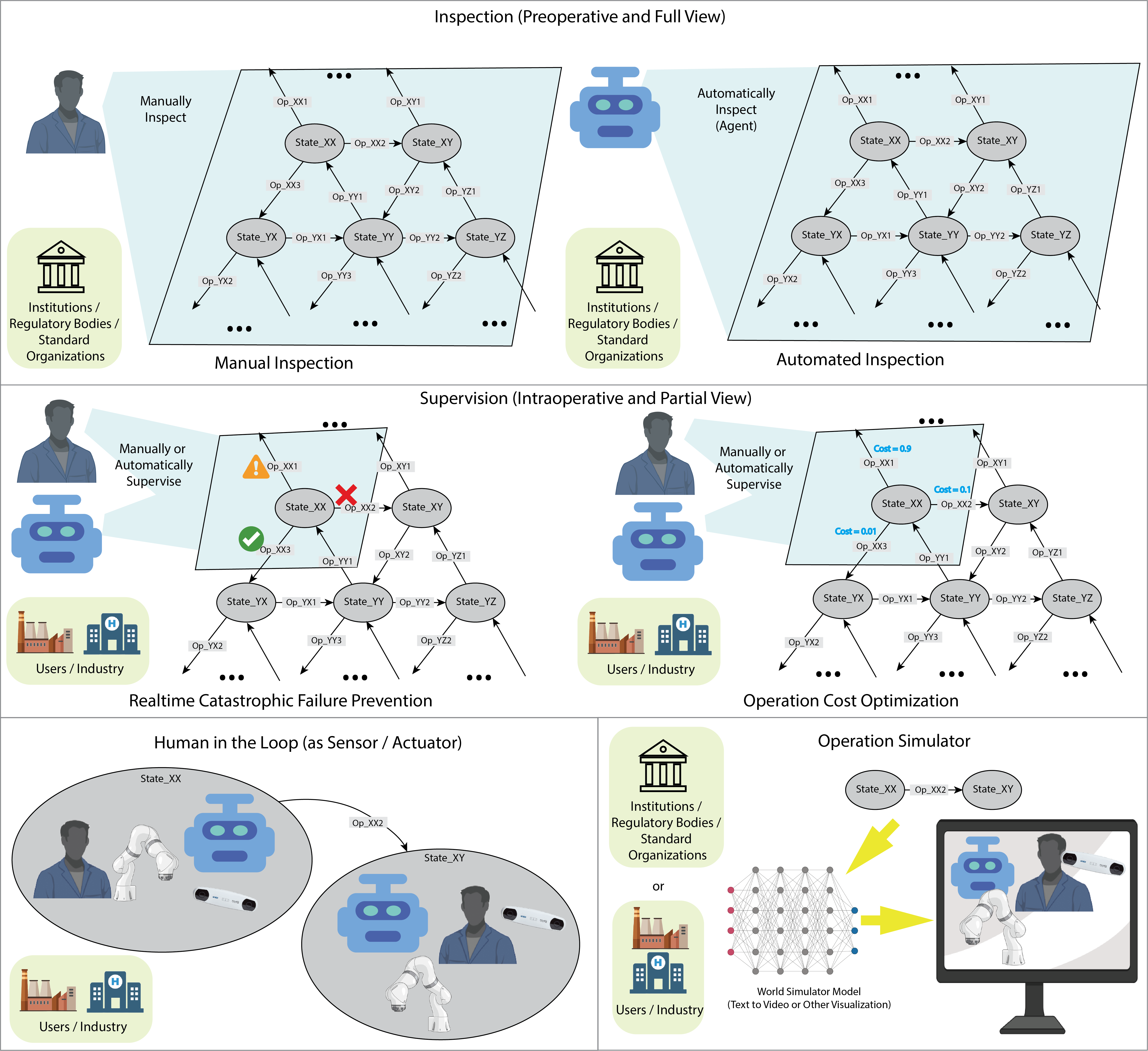
Automated and Regulated Robotic Systems
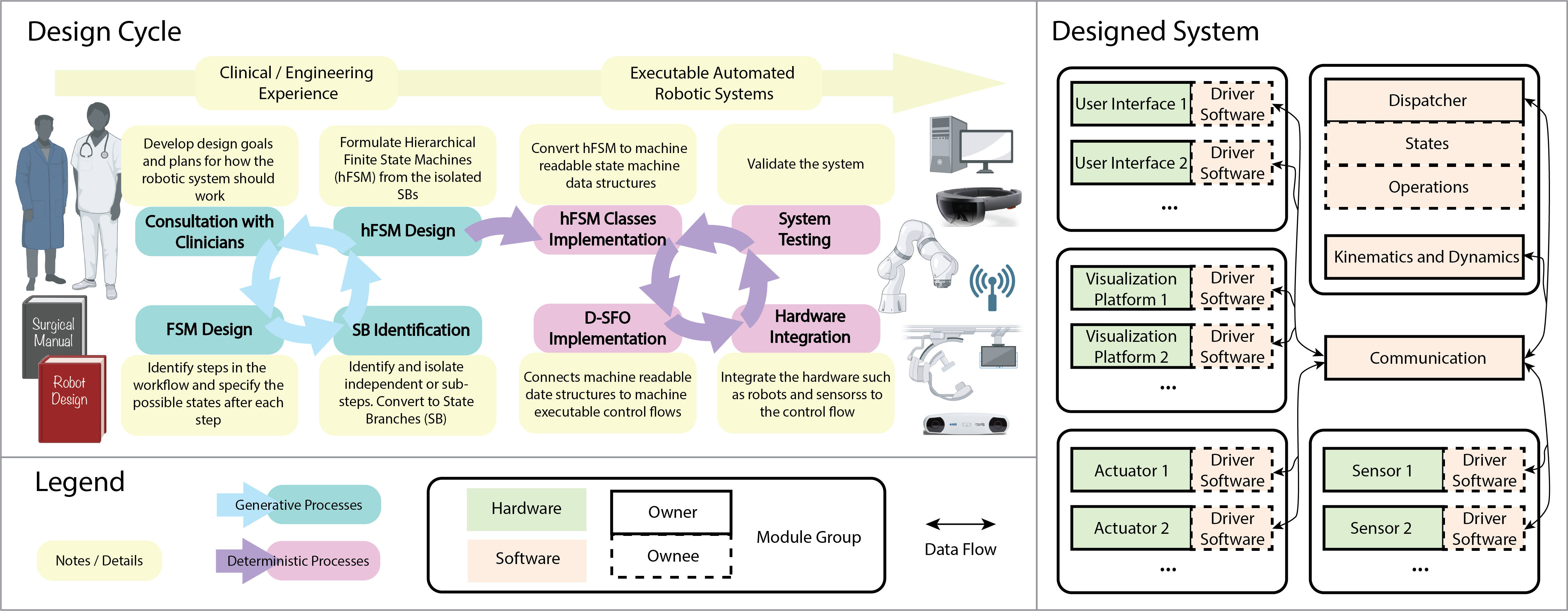
The rapid development of generative technology opens up possibility for higher level of automation, and artificial intelligence (AI) embodiment in robotic systems is imminent. However, due to the blackbox nature of the generative technology, the generation of the knowledge and workflow scheme is uncontrolled, especially in a dynamic environment and a complex scene. This poses challenges to regulations in safety-demanding applications such as medical scenes. We argue that the unregulated generative processes from AI is fitted for low level end tasks, but intervention in the form of manual or automated regulation should happen post-workflow-generation and pre-robotic-execution. Development: Python
Publications:
|
1 Sensing, Tracking, and Machine Vision
Sensing and Tracking
|
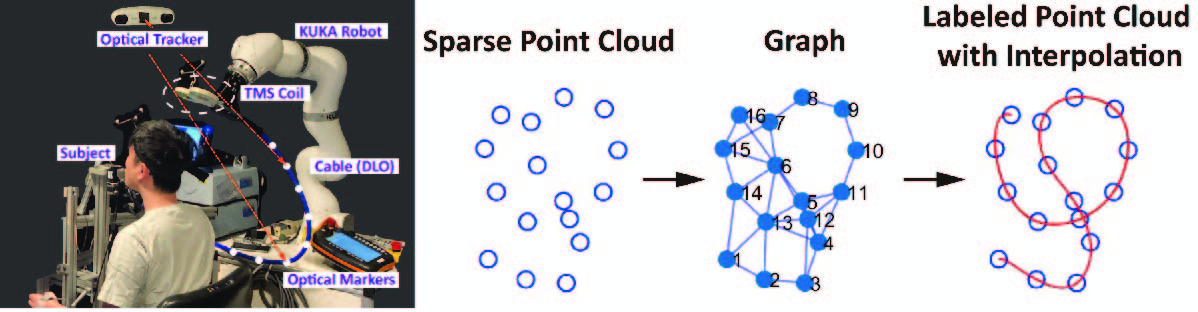
Shape Estimation of Deformable Linear Object
Realtime shape estimation of continuum objects and manipulators is essential for developing accurate planning and manipulation paradigms. The existing methods that create dense point clouds from camera images, and/or use distinguishable markers on a deformable body have limitations in realtime tracking of large continuum objects/manipulators and the physical occlusion of markers can often compromise accurate shape estimation. We propose a robust method to estimate the shape of linear deformable objects in realtime using scattered and unordered key points. Development: Python, Matlab, ROS
Publications:
|
|
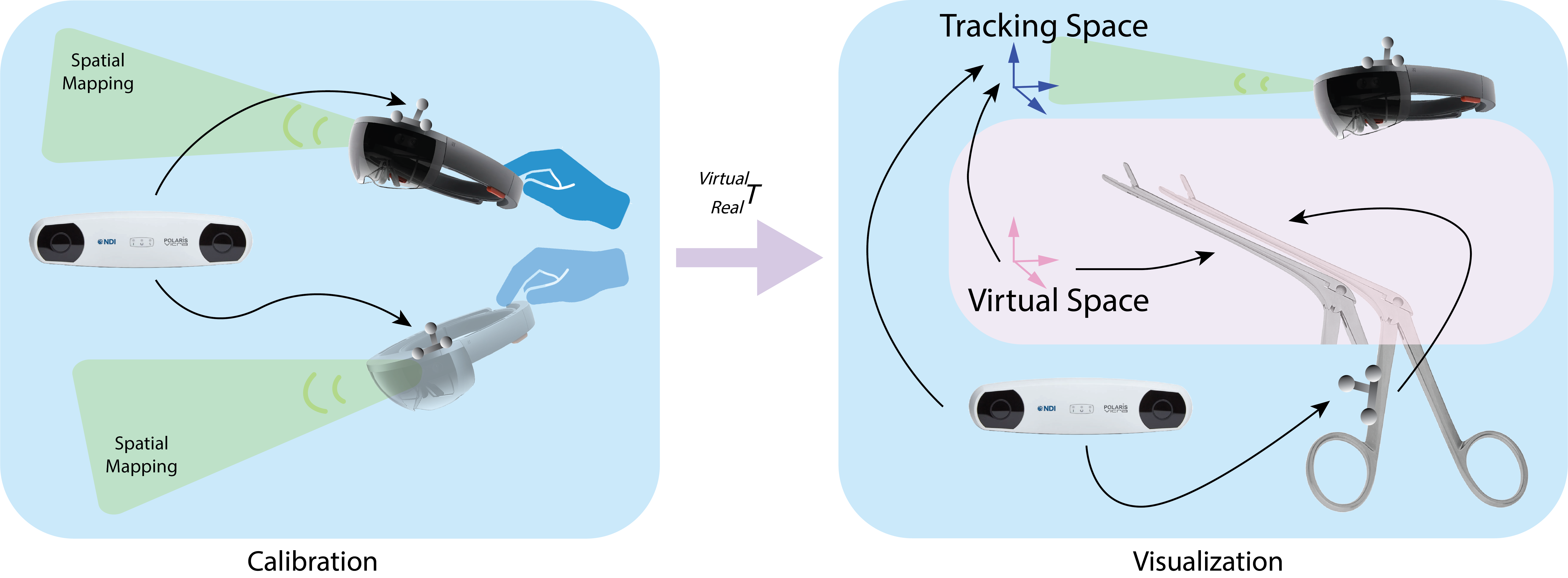
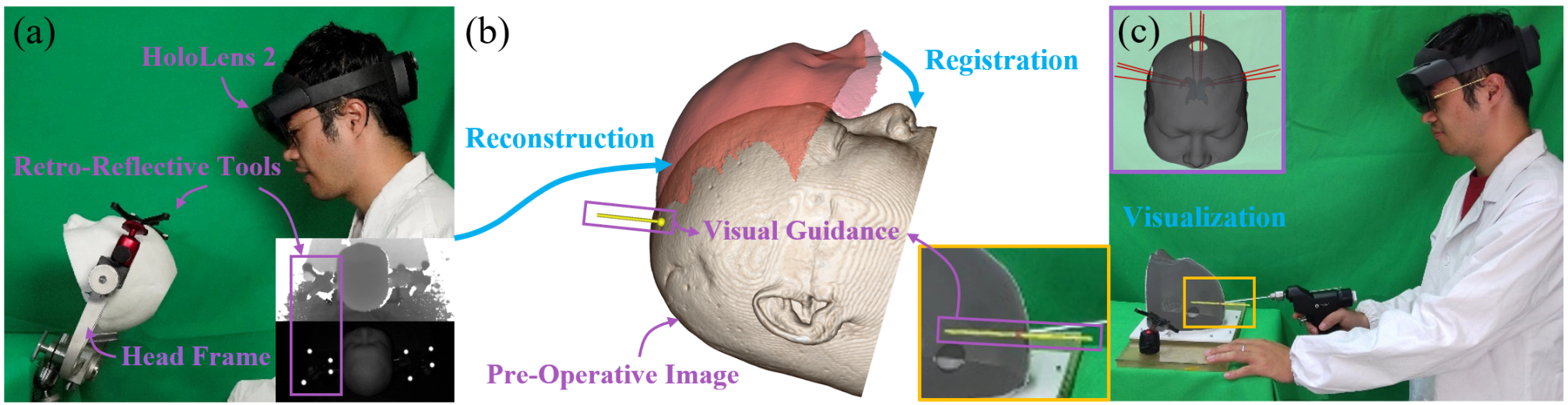
Virtual-to-real calibration method in head mounted displays
We propose a simple virtual-to-real calibration method based on retroreflective optical markers, that combines an external optical tracker and a built-in accurate tracking system for MR-HMDs. [1] To further simplify the process, we also design a new virtual-to-real calibration method combining the off-the-shelf self-location algorithm in HMDs. [2] Development: C++, Python, ROS, C#, Unity
Publications:
|
|
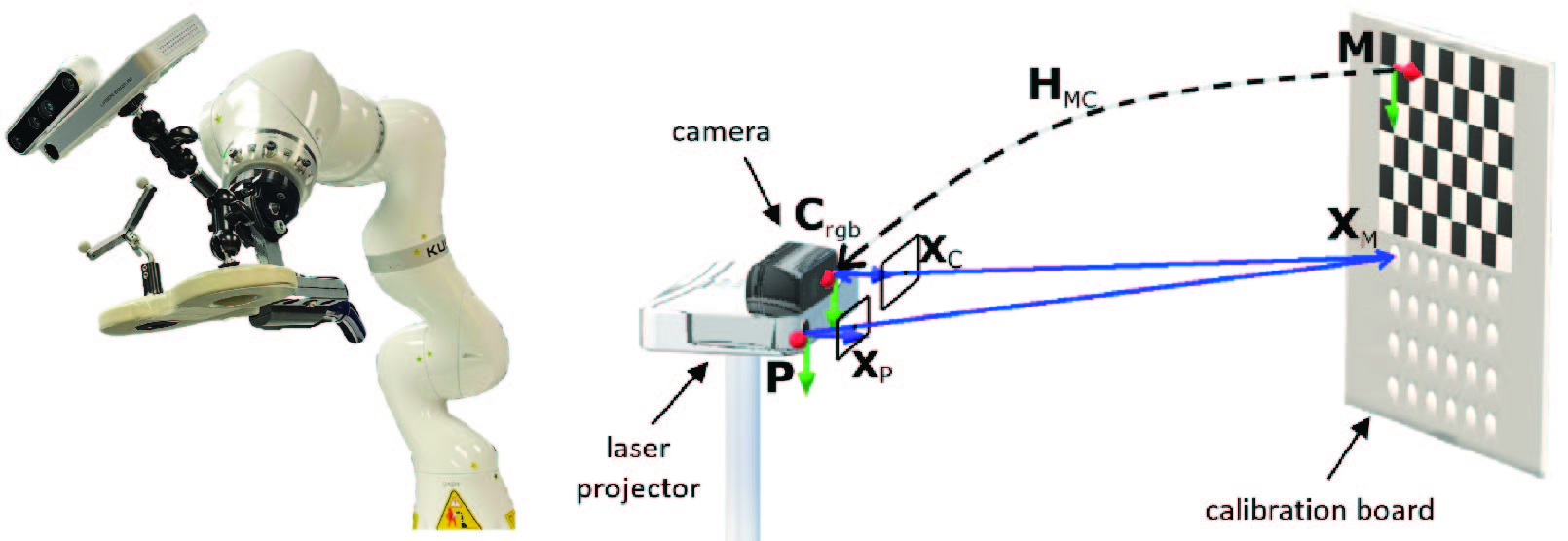
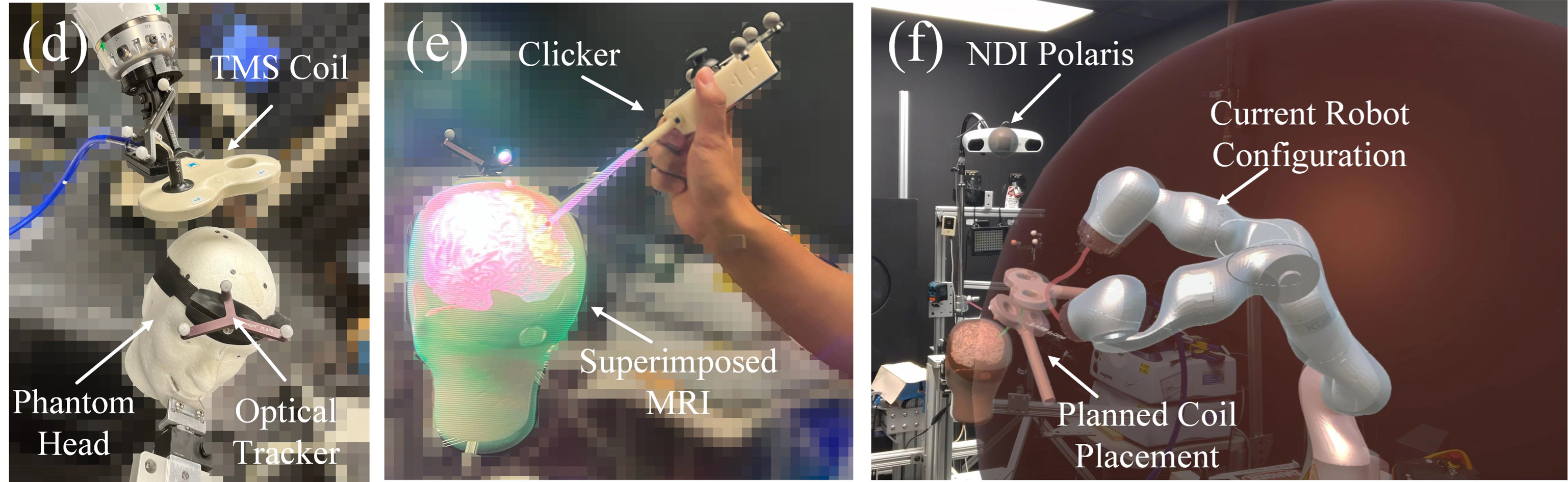
Projection Mapping and Tracking
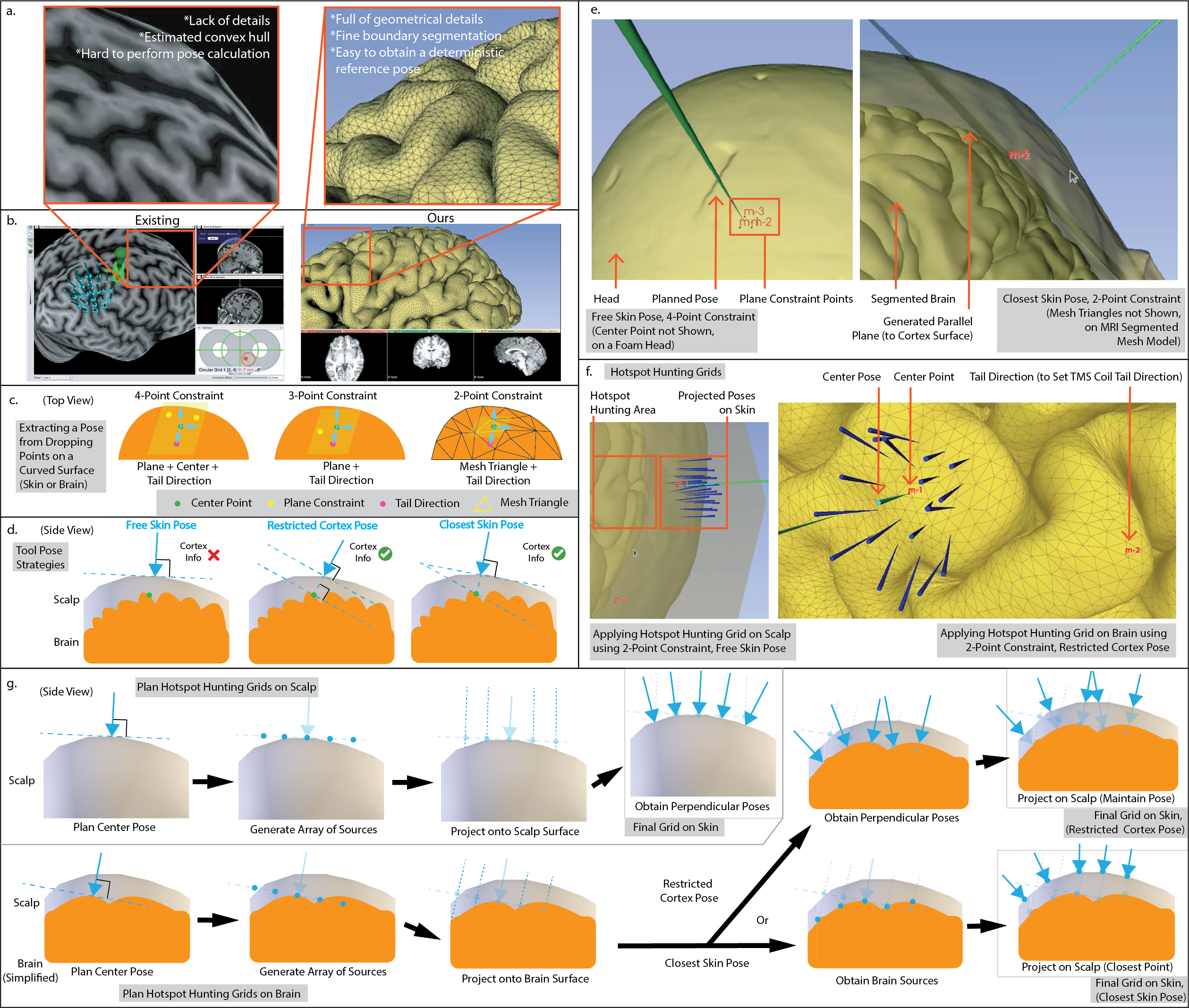
This work presents two system improvements for robot-assisted TMS (RA-TMS) application. Previous systems have used outside-in tracking method where a stationary external infrared (IR) tracker is used as a reference point to track the head and TMS coil positions. This method is prone to losing track of the coil or the head if the IR camera is blocked by the robotic arm during its motion. To address this issue, we implemented an inside-out tracking method by mounting a portable IR camera on the robot end-effector. PPMD can track the head via an IR tracker, and can project a planned contact point of TMS coil on the head or overlay the underlying brain anatomy in real-time. Development: C++, Python, ROS, Vtk
Publications:
|
Markerless Tracking
2 Medical Robotics
Intelligent Medical Robots
|
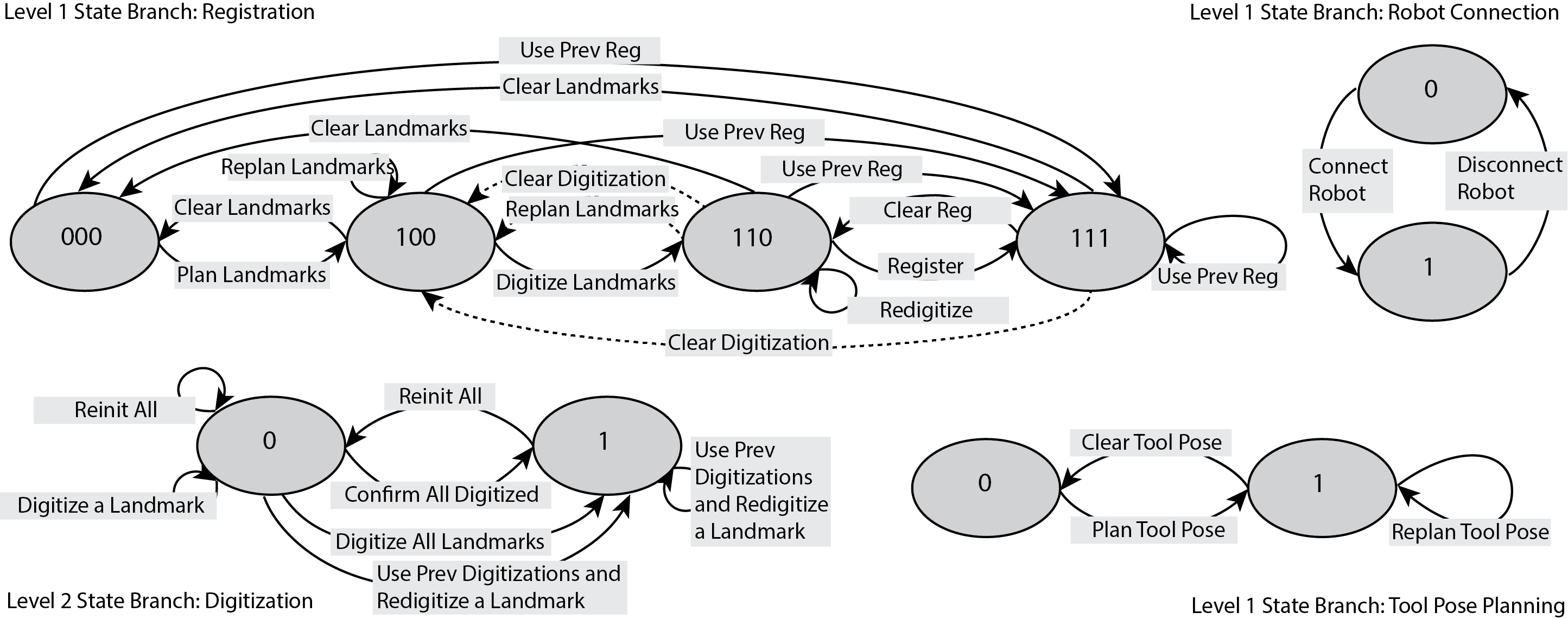
Process Controlled Medical Robots
"Medical errors, defined as unintended acts either of omission or commission that cause the failure of medical actions, are the third leading cause of death in the United States. Medical errors can include communication breakdowns, diagnostic errors, poor judgment, and inadequate skills. The application of autonomy and robotics can alleviate some causes of medical errors by improving accuracy and providing means to preciously follow planned procedures. However, for the robotic applications to improve safety, they must maintain constant operating conditions in the presence of disturbances, and provide reliable measurements, evaluation, and control for each state of the procedure. " [1] Development: C++, ROS
Publications:
|
Systems for Robot Assisted Procedures
|
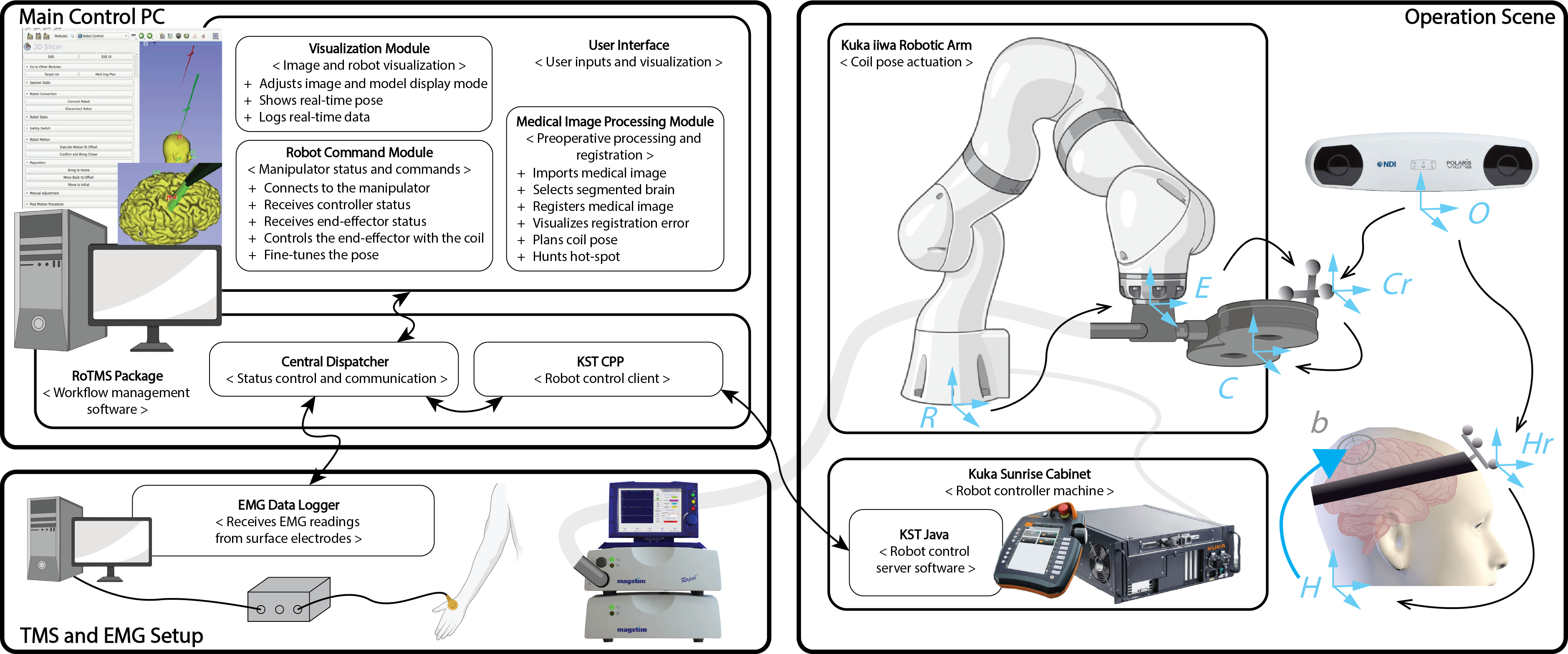
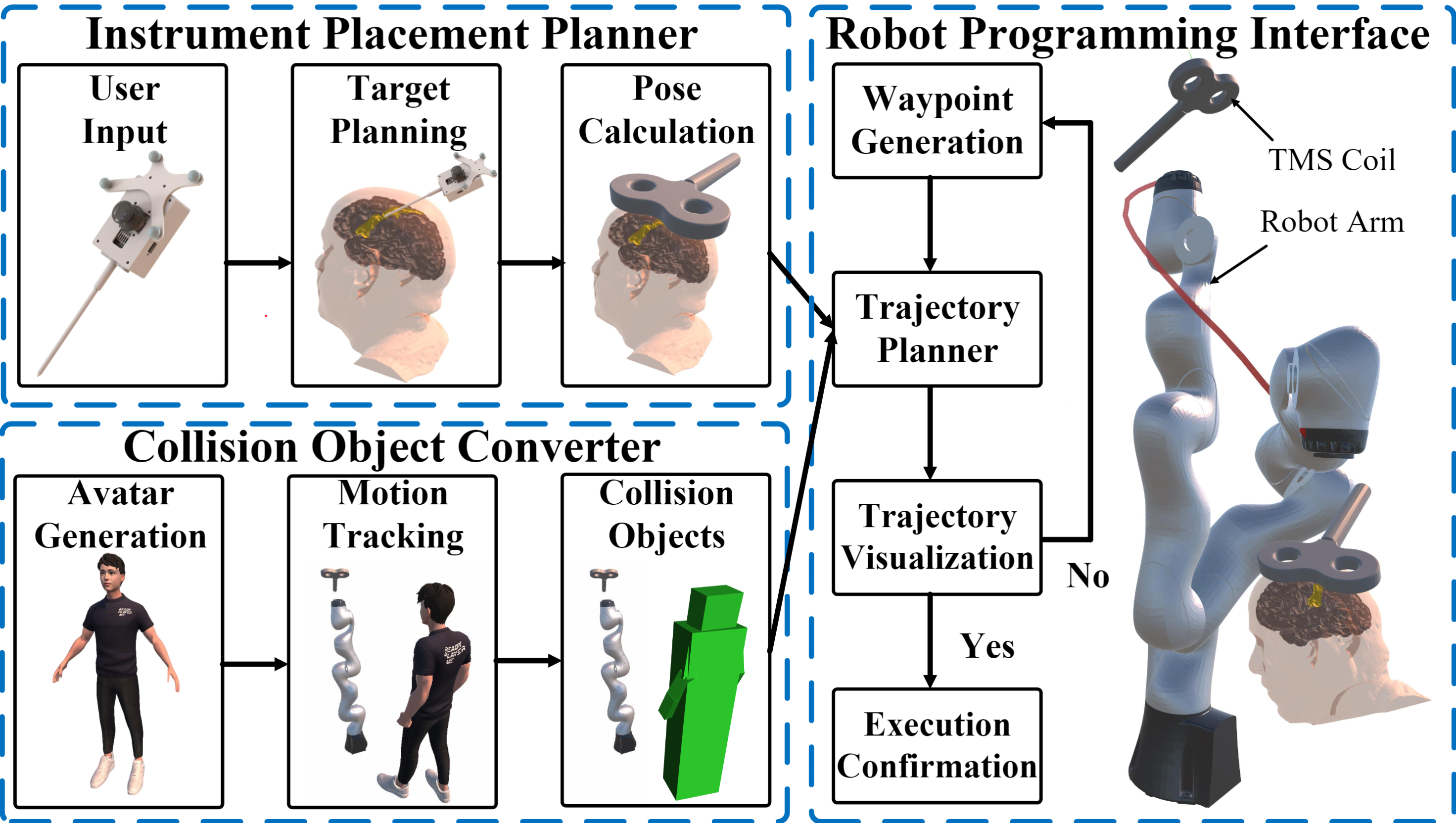
Robotic Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
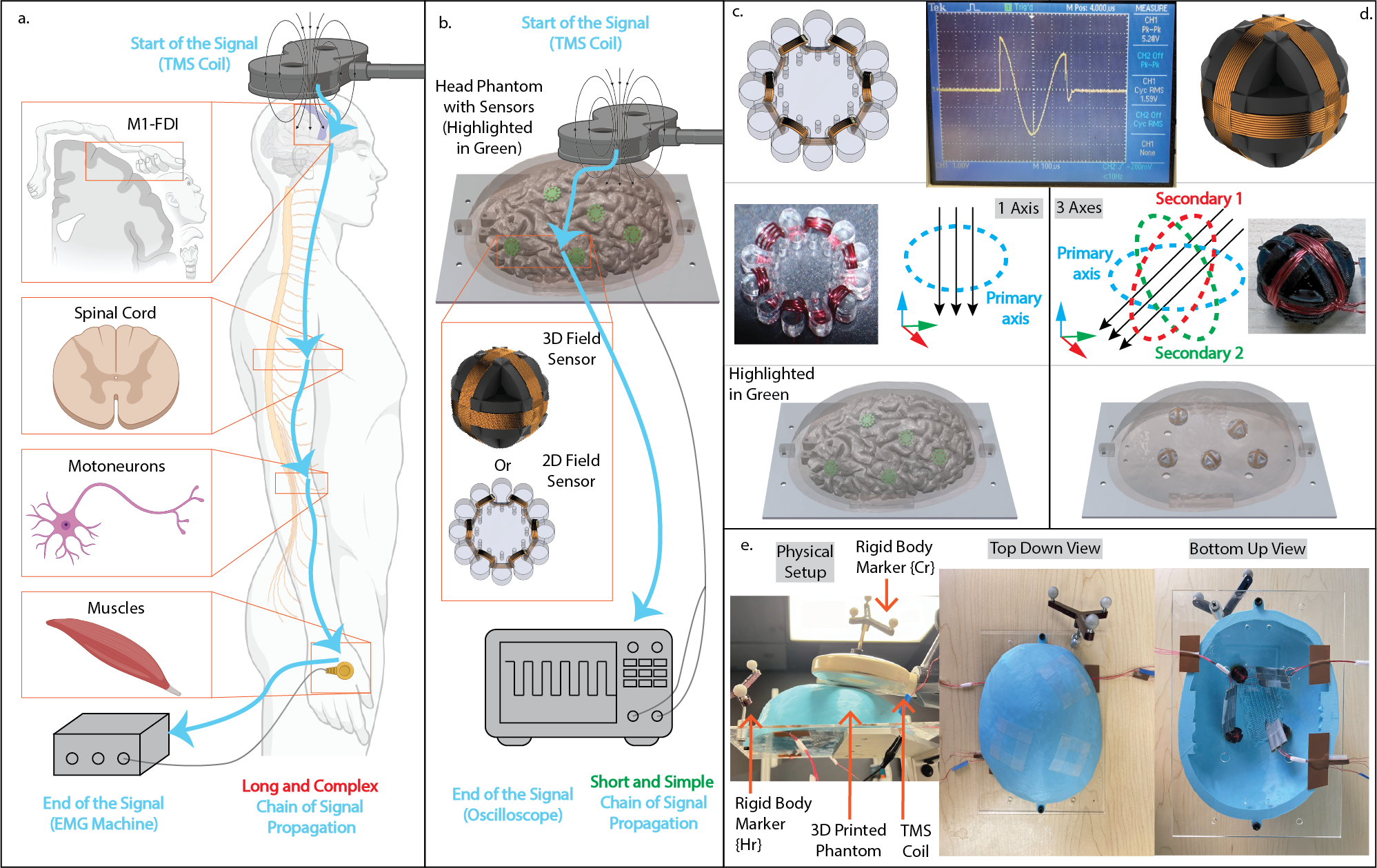
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) is a neurostimulation technique that relies on electromagnetic induction to generate an electric field in the brain, with applications in both research and clinical settings. Achieving an optimal neuro-modulatory effect requires accurate placement and orientation of the TMS coil on the head. The use of a robotic method can enhance accuracy and streamline the procedure for placing the TMS coil. Development: C++, Python, Matlab, ROS, Unity, Vtk, 3D Slicer
Publications:
|
|
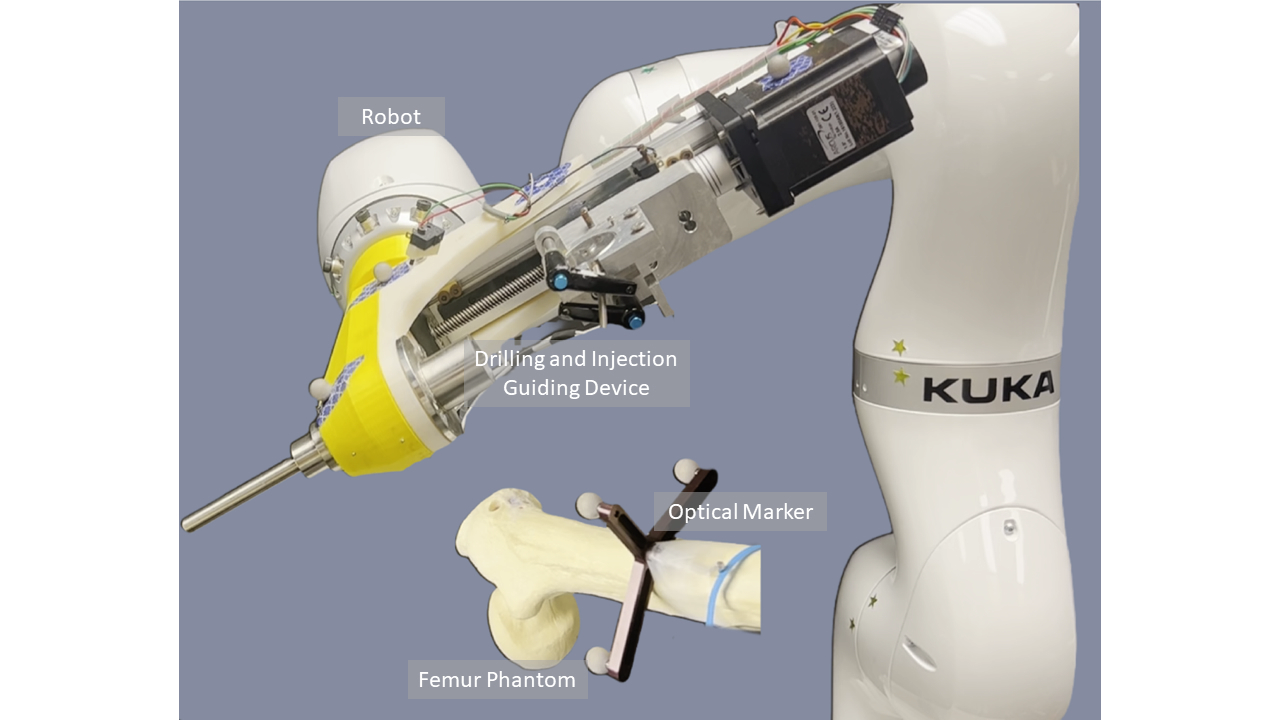
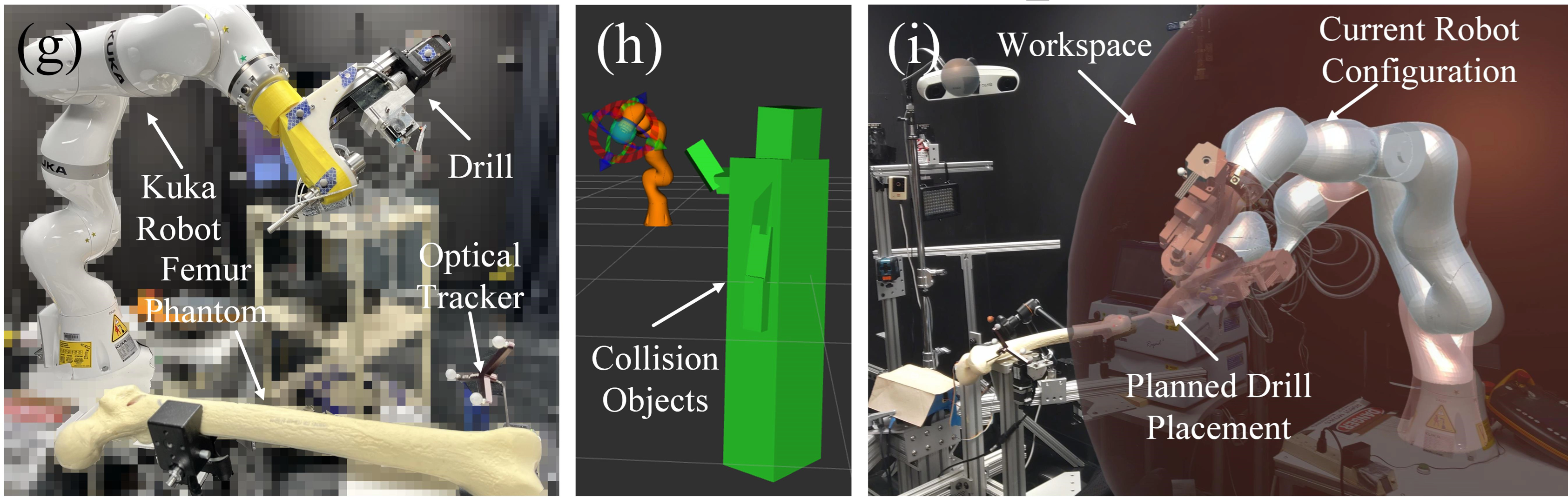
Robot-Assisted Femoroplasty
Osteoporotic hip augmentation is the medical intervention to reinforce hip bone and reduce the risks of hip fracture. It is commonly performed on patients who suffer from osteoporosis. The procedure uses bone cement inside hip joint. During cementoplasty, surgeons drill the femur from the entry point on the greater trochanter surface, and inject bone cement to the femuroal neck. Robotic system has the potential to enhance accuracy and improve surgery results. Development: C++, Python, ROS, Vtk, 3D Slicer
Publications:
|
Robot Kinematics and Dynamics
|
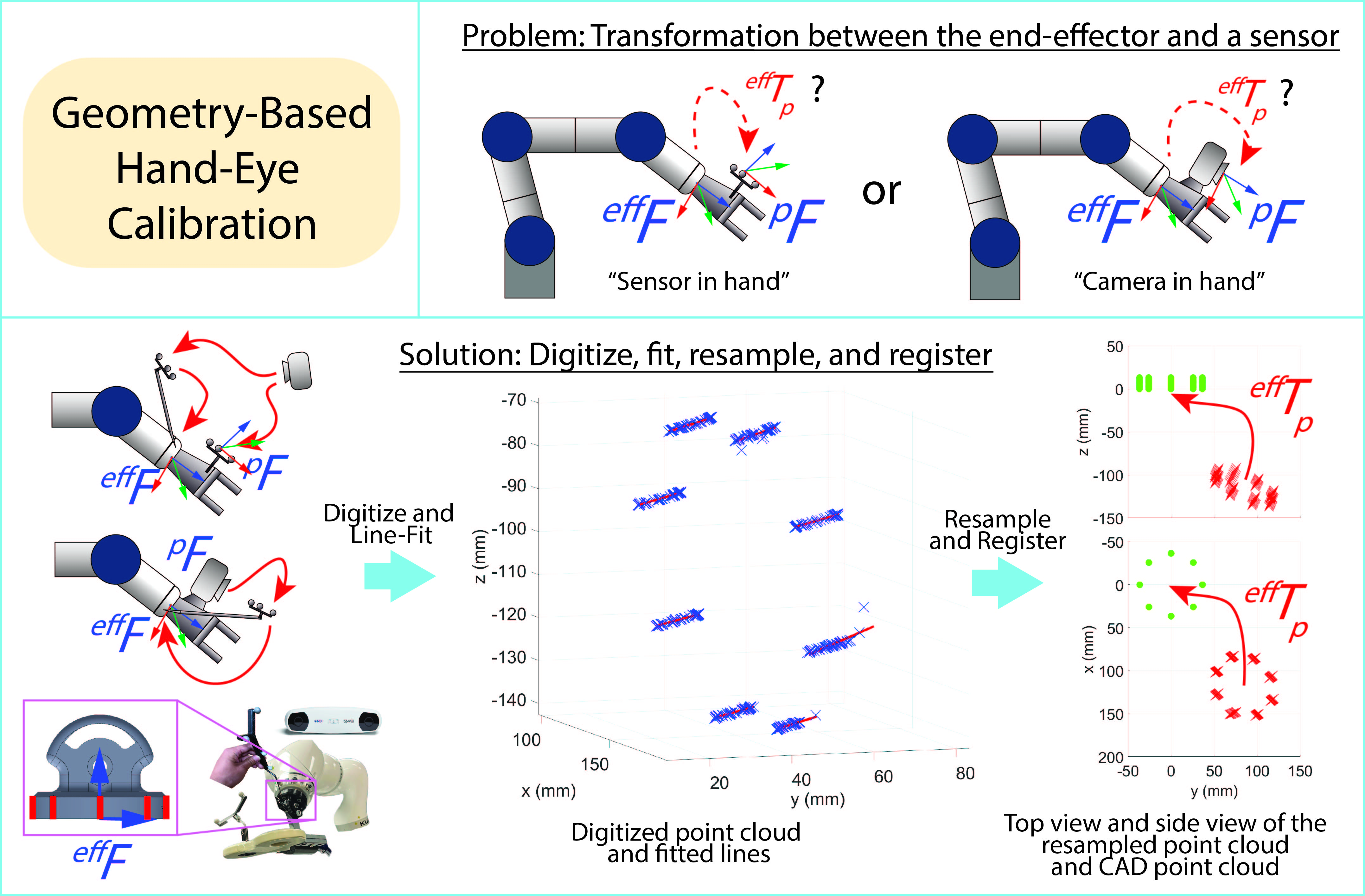
Robot Kinematics
Robot kinematics is the study of movements. The robotic systems rely on good modeling and accurate calibration results. Applications such as medical and surgical robotics are especially accuracy-demanding. We conduct these fundamental studies for better development of reliable and robust systems. Development: C++, ROS
Publications:
|
3 Medical Augmented Reality
Systems for AR Assisted Procedures
|
Augmented Reality Assisted Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
Also see TMS. Mixed Reality can provide immersive visualization with crucial information in medical procedures. TMS, a neuromodulation technique, requires accurate tracking data to produce desired modulation results. In addition, the overlay of anatomy, simulated electromagnetic fields, neuro pathways will aid the operator in decision making during the procedure. Development: Unity, C#, ROS, C++
Publications:
|
|
Augmented Reality Assisted Femoroplasty
Also see femoroplasty. The capability of Mixed Reality, especially virtual object overlay and focus and context, can help with surgical scene understanding. In addition, in robotic surgery, the robot path planning and execution can use Mixed Reality to promote security and mindful human-machine interaction. Development: Unity, C#, ROS, C++
Publications:
|
|
Augmented Reality Assisted Orbital Floor Reconstrution Surgery
Conventionally, the accuracy of implant placement relies on the surgeon’s expertise. Intraoperative imaging and navigation are rarely used due to their cost and setup times, so erroneous implant positioning is often unrecognized until postoperative imaging. This confers risk to the patient’s eyeball, orbital vasculature, optic nerves, and stereotactic vision. In this work, we develop the workflow and user interface of an Augmented Reality (AR) system to aid surgeons with intraoperative placement of an orbital floor implant and ultimately reduce rates of implant malposition. Development: C#, Python, Unity Publications:
|
4 Medical Imaging
Image Segmentation
|
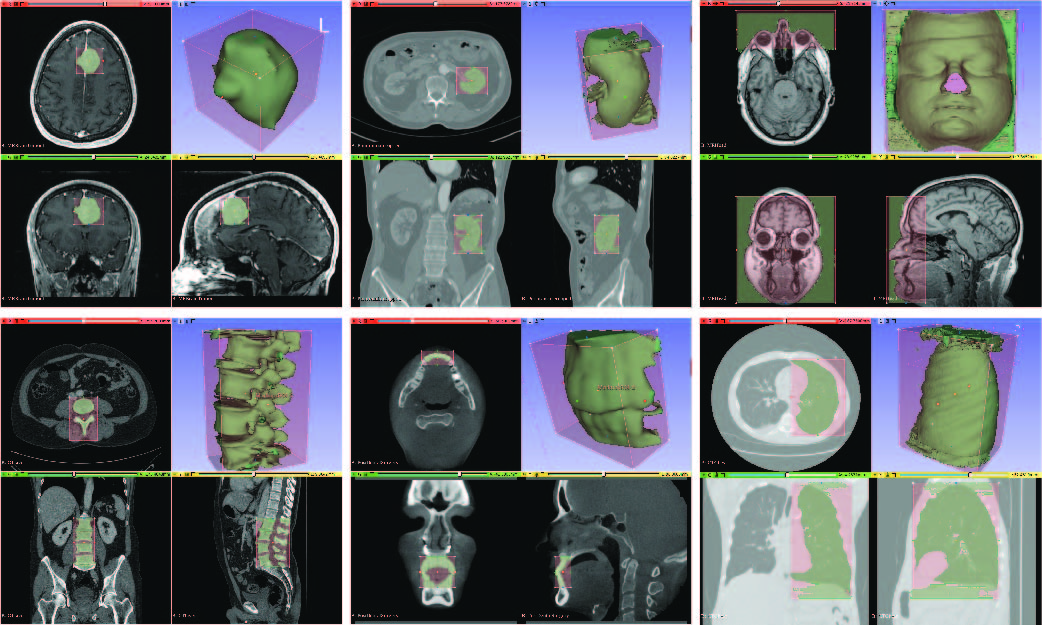
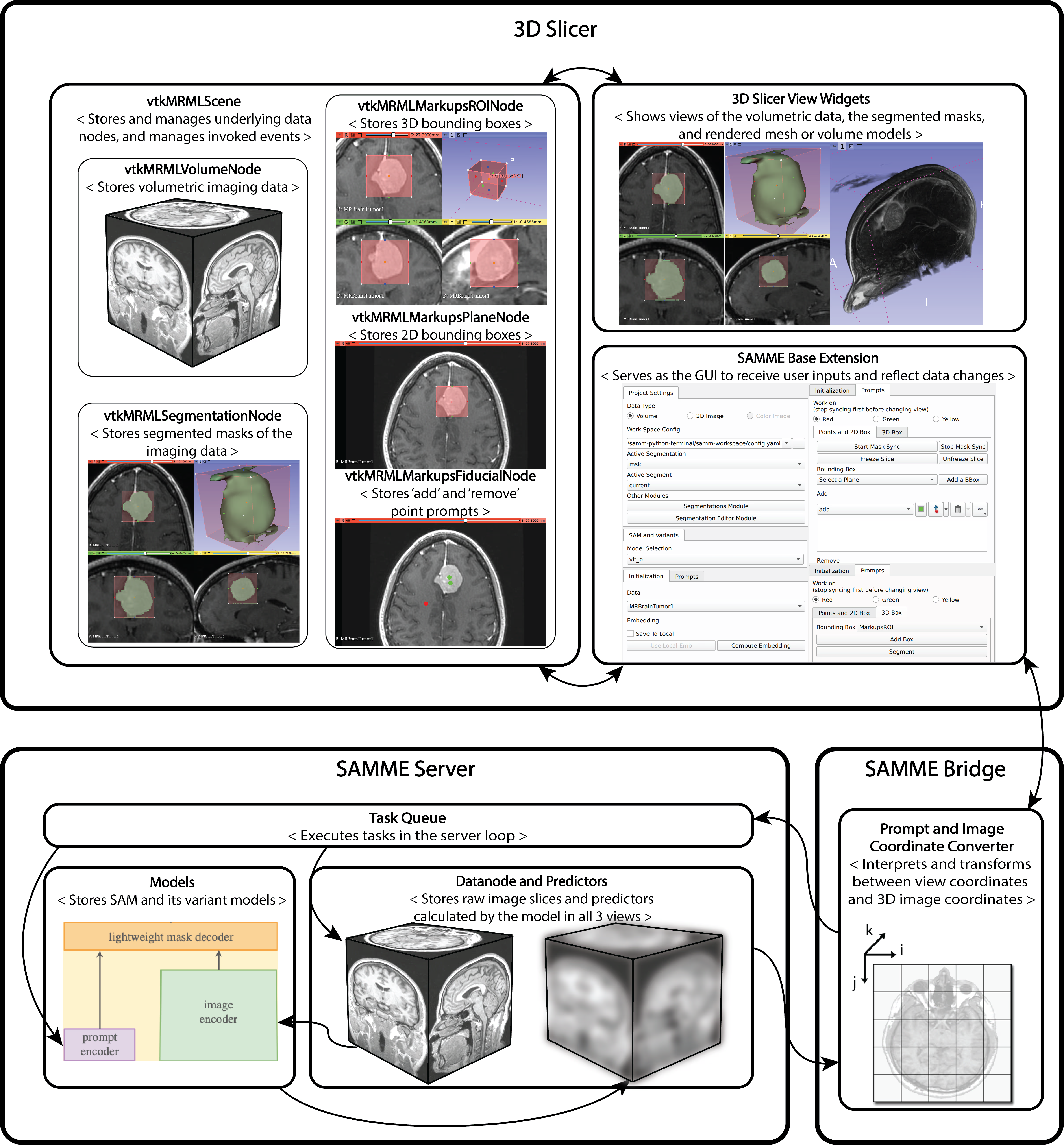
SAM Integration on 3D Slicer
The Segment Anything Model (SAM) is a new image segmentation tool trained with the largest segmentation dataset at this time. The model has demonstrated that it can create high-quality masks for image segmentation with good promptability and generalizability. However, the performance of the model on medical images requires further validation. To assist with the development, assessment, and utilization of SAM on medical images, this research introduce Segment Any Medical Model (SAMM), an extension of SAM on 3D Slicer, a widely-used open-source image processing and visualization software that has been extensively used in the medical imaging community. Development: Python, 3D Slicer
Publications:
|
Spatial Reconstruction
|
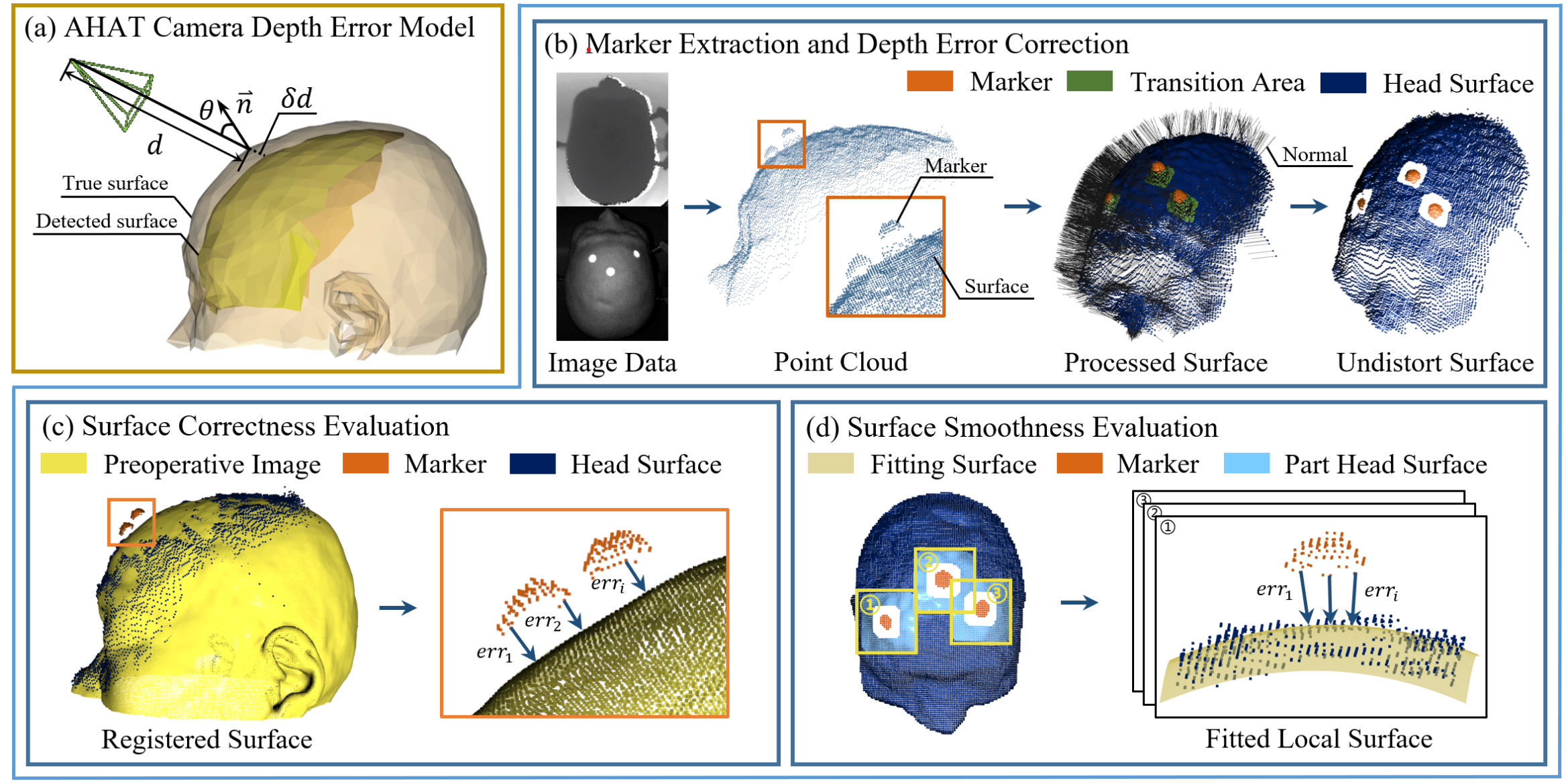
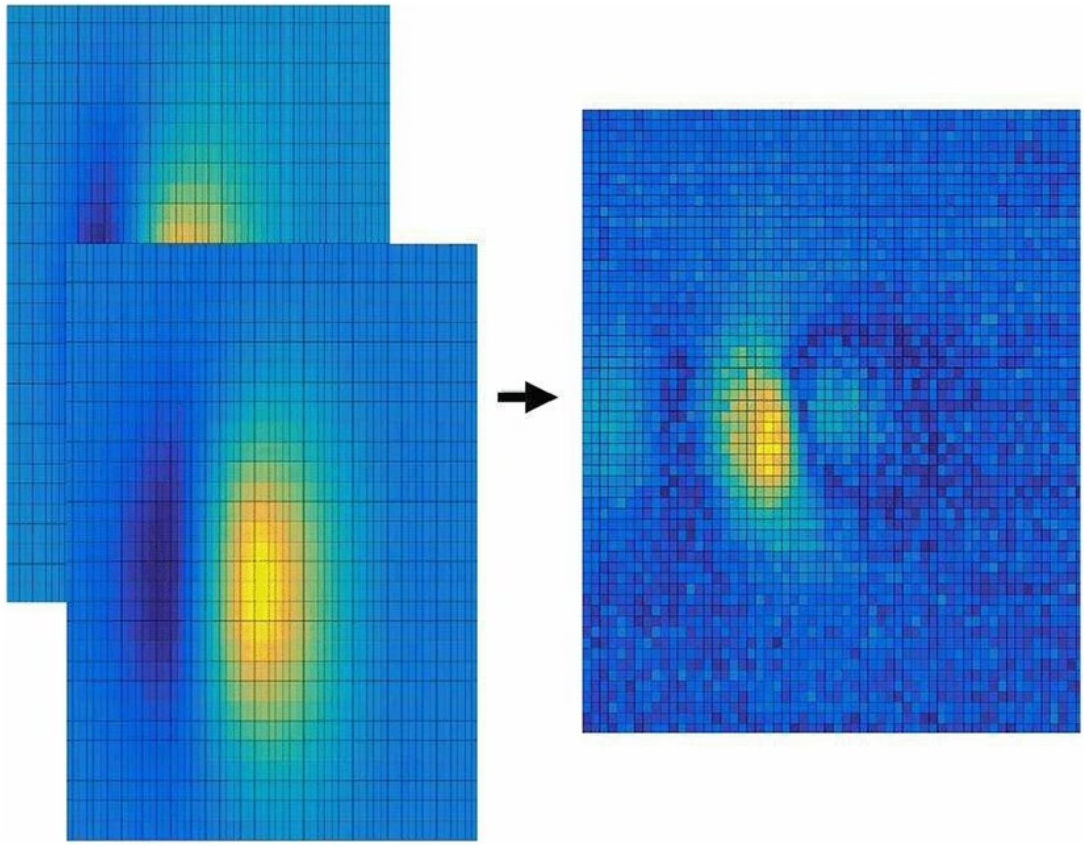
Spatial Reconstruction for Anatomy Tracking
"A tracking pipeline combining retro- reflective markers and point clouds is then proposed for accurate head tracking. The head surface is reconstructed using depth data for spatial registration, avoiding fixing tracking targets rigidly on the patient’s skull." [1]
Publications:
|
5 Neuroscience
Autokinetic Effect
|
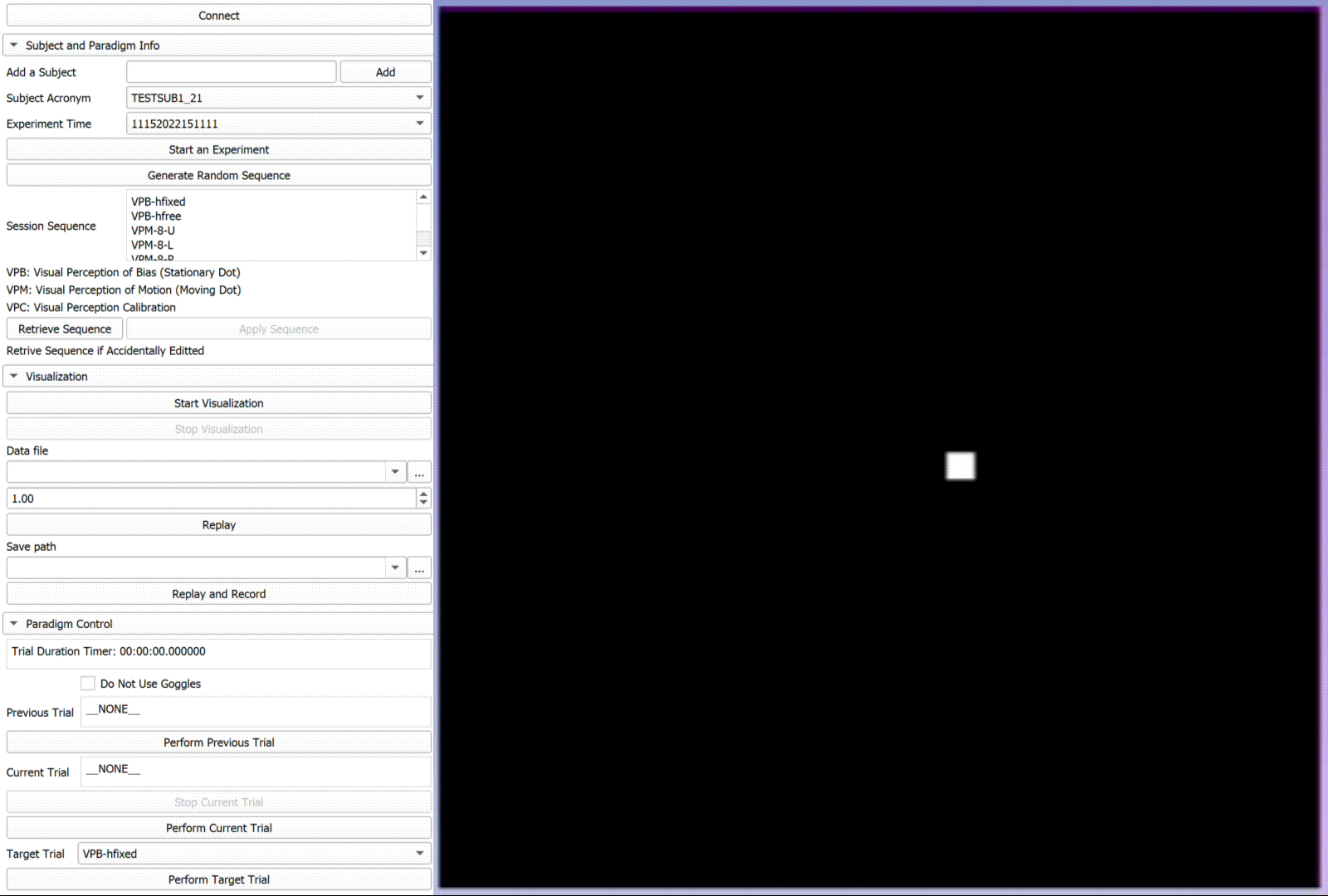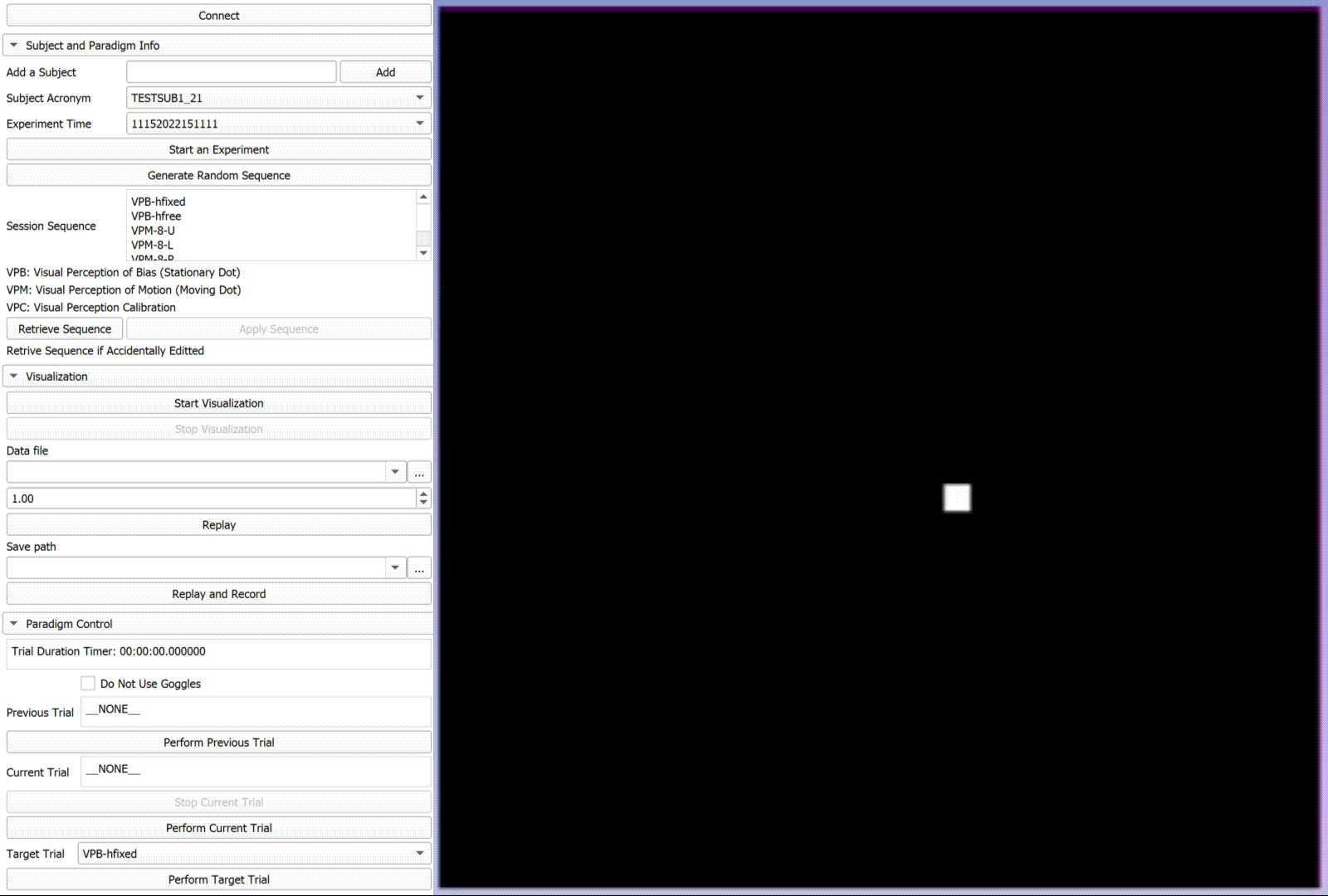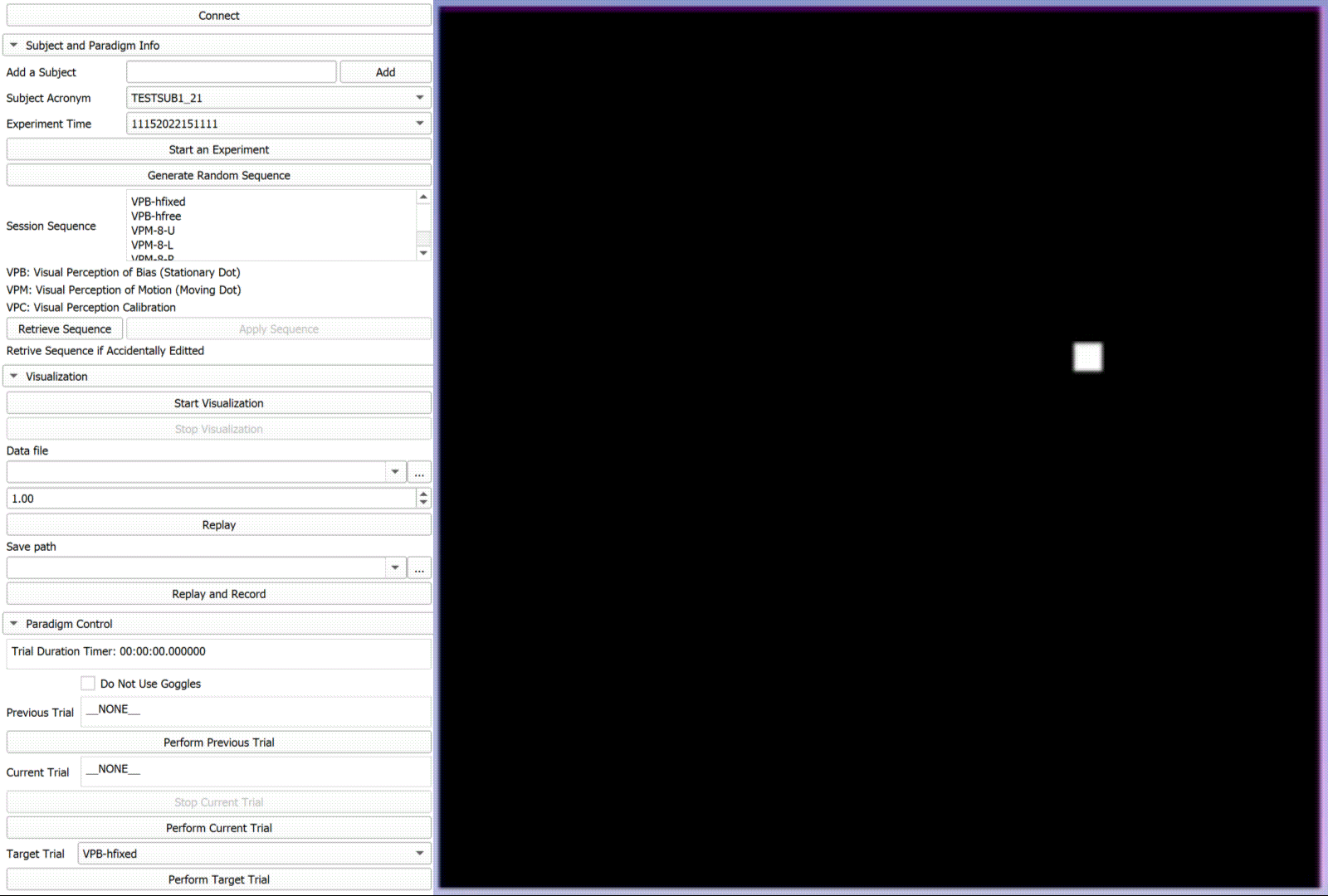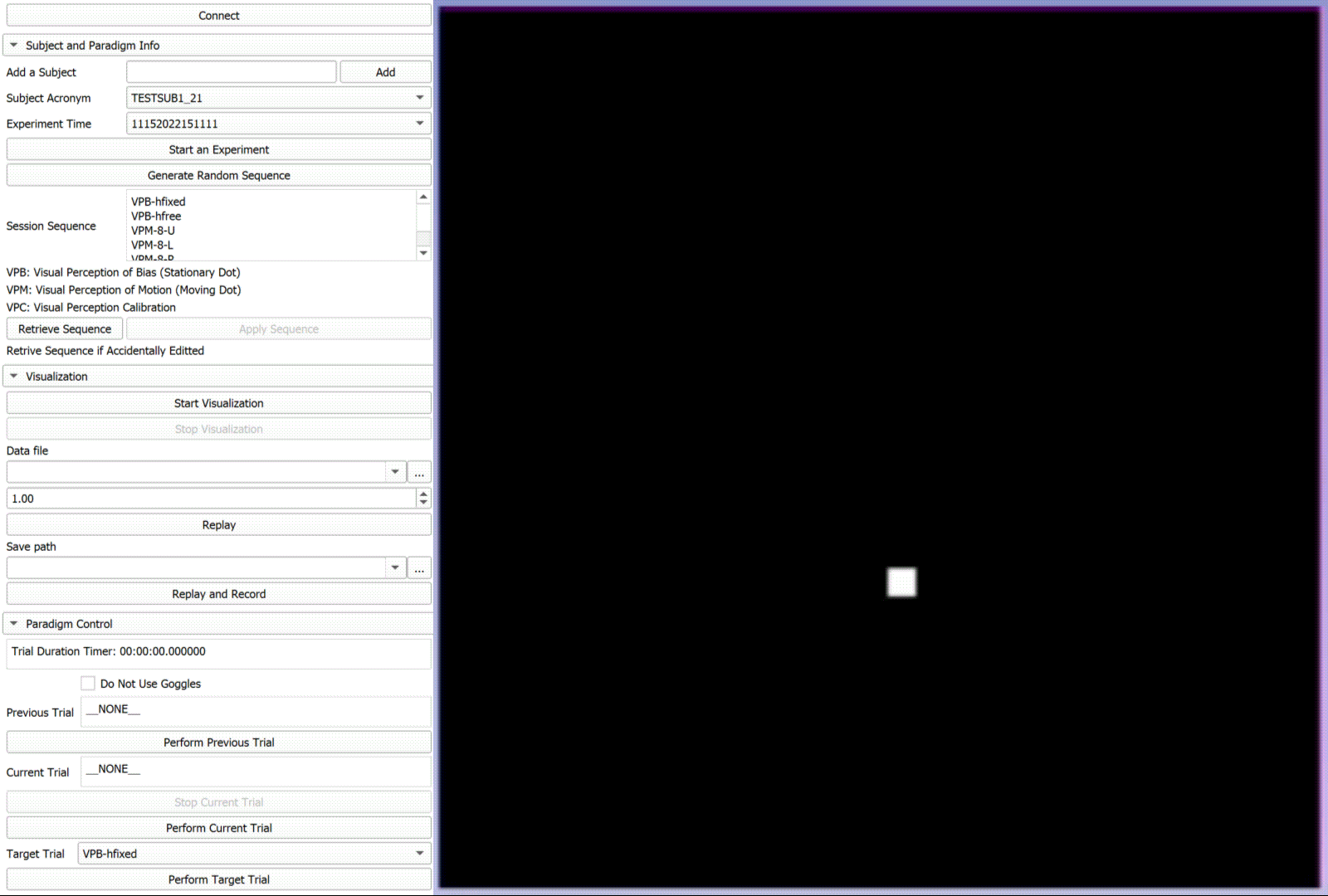
Autokinetic Effect of Human Subjects
"In natural viewing conditions, the brain can optimally integrate retinal and extraretinal signals to maintain a stable visual perception. These mechanisms, however, may fail in circumstances where extraction of a motion signal is less viable such as impoverished visual scenes. This can result in a phenomenon known as autokinesis in which one may experience apparent motion of a small visual stimulus in an otherwise completely dark environment. In this study, we examined the effect of autokinesis on visual perception of motion in human observers. We used a novel method with optical tracking in which the visual motion was reported manually by the observer. " [2] Development: C++, ROS, Matlab, Python, 3D Slicer
Publications:
|
6 Past Research
|
Pulsed Eddy Current Data Analysis for the Characterization of the Second-Layer Discontinuities
The pulsed eddy current (PEC) technique has proven effective in identifying concealed flaws within metallic structures. Typically, specific time-domain features are utilized to analyze PEC data, including peak value, intersection lift-off point, rising point, crossing time, and differential time to peak. This study builds upon prior research that focused on identifying radial cracks originating from fastener holes in the second layer of a two-layer mock-up aircraft structure. Development: Python, Keras
Publications:
|
|
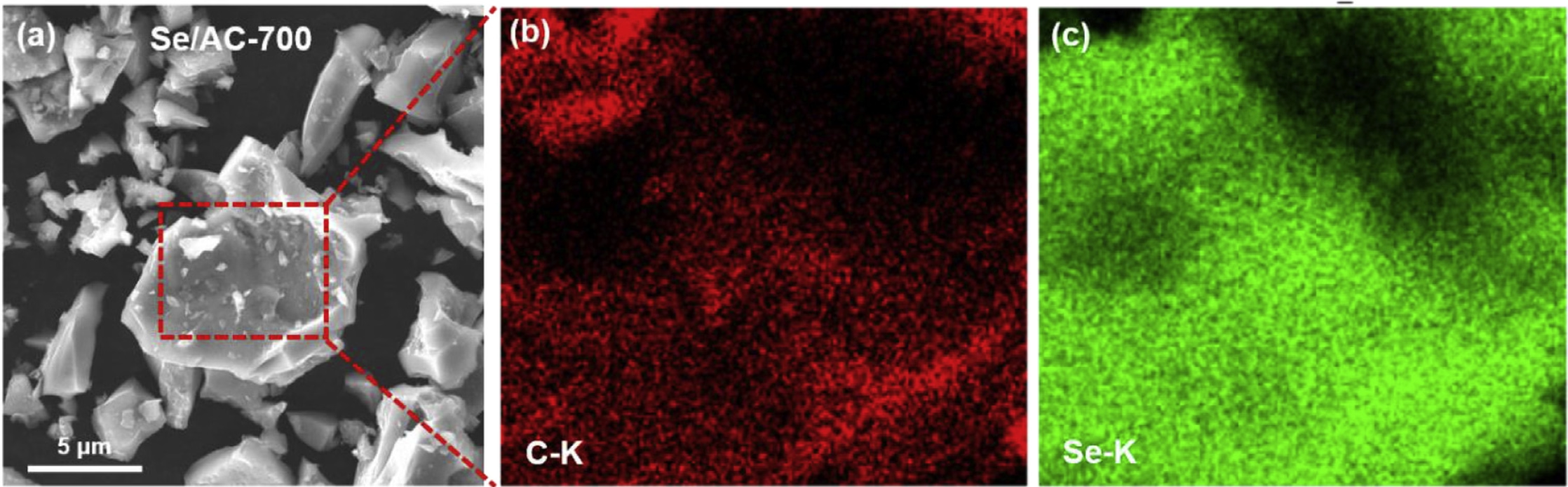
Lithium Batteries with Bio-waste Derived Activated Carbon
Lithium-selenium (LieSe) batteries hold significant potential as an energy storage solution, thanks to selenium's cathodic advantages such as high electronic conductivity and volumetric energy density. The pivotal factor in optimizing Se cathodes for high-performance Li-Se batteries lies in the design of porous carbon with an adjustable structure at an affordable cost. This research focuses on creating hierarchically microporous activated carbon (AC) derived from discarded coffee grounds through a carbonization and KOH-activation process.
Publications:
|